Website test tools are more and more popular and become one of the best assistants to website developers as well as other relative parties. Through the numbers, reports, and results of the test tool, you will know what problems your website has and find a way to eliminate them. However, there are some common misconceptions around these website speed test. What are they?
- How to Quick Test Internet Speed
- Common internet broadband complaint & Solution
- Check Internet Outage: Tips for Better Internet Connection

Common misconceptions of website test tools
What are website test tools?
Website test tools are the name given to software testing on website performance. These tools will help you identify issues of your website before the system is revealed to the public or solve them in time when it was launched and had issues.
Problems a website can get could be the security of the web application, the basic functionality of the site, its accessibility to handicapped users and fully able users, Cross browser testing, and operating systems, as well as readability of the website, and the ability to survive a massive spike in user traffic, both of which are related to loading time page testing.
There are a lot of website test tools both free and paid money. Each tool has unique features in order to attract users. Some famous website speed test you can trust to use are MySpeed, GTMetrix, Pingdom, etc.
MySpeed is one of the most famous website test tools you can trust to use
Most website performance testing tools are simple to use. Everyone can run the test and check their sites without full of specific website knowledge. You just enter the URL of your site and wait for a couple of minutes to get the results. Not only check the website performance but you also can get tracks of how it's doing over time which helps you observe and improve the quality of your website.
The misconceptions of website test tools
Running the website test tools is simple, but there are still some misconceptions around the results which are shown to users. Today, MySpeed will help you understand more and avoid those misconceptions as well as the ways to optimize your website.
Average time on page
The average stay on-page is a useful metric for measuring a user's interest in your site's content, whether they're actually reading your content or not. This index can cause some misleading to website analyzers especially if the page is a page with a high bounce rate.
To understand and avoid this misconception when using the website test tools, let’s find out how Google Analytics calculates the time spent on the website. In detail, Google Analytics measures how long a user stays on a website by taking the time a user visits the page subtract the time a user visits and reads the content of the page while a bounce is calculated when a visitor visits another site on the website.

Google Analytics measures how long a user stays on a website by taking the time a user visits the page subtract the time a user visits and reads the content of the page while a bounce is calculated when a visitor visits another site on the website
For example, user A starts on Page 1, then goes to Page 2 and the amount of time spent on Page 1 is counted as 45 seconds. It is the time user A leaves Page 1 and goes to Page 2 However, user B just only looks at Page 1 and then exits the website, so even though he stayed on Page 1 for a while, Google cannot calculate how long.
This will be very bad for landing pages or helps resources, which focus on providing visitors all necessary information in a single visit. For instance, a prospect finds your interesting blog post on Google, reads it completely in 20 minutes, and subscribes to your newsletter via a popup before closing the browser tab. This visit would not be counted in your time on page metric at all.
Consequently, if a user does not visit another website on that website, then Google cannot calculate this value. Google will not know how long a user has stayed on that page, so they stay on a page is assigned 0 by Google. As a result, the user's Average Time spent on the page is incorrect.
Solution:
To solve this issue, you can insert a short Javascript code on the website in order to every 15 seconds the website will connect the Google Analytics if the user is still on-page. After that, you will create a Custom Report on Google Analytics to observe the differences between Average Engagement and Average time on page ( what Google calculate and what you adjusted).
To solve this issue, you can insert a short Javascript code on the website in order to every 15 seconds the website will connect the Google Analytics if the user is still on-page
In addition, you should tie up your content on your website, optimize images as well as the readability to increase the average time on page. The truth is, the ideal average for time on page will vary. Some marketers conclude that their average time on the page should be between 2 - 3 minutes. However, others dial into this metric using read time, which is averaged based on the number of words in an article and a general reader’s words per minute speed. In that scenario, the time visiting a page from 40 to 50 seconds is encouraging.
Bounce rate
Another misconception when using website test tools is the Bounce rate. This is one of the most commonly referenced metrics used to evaluate a website's quality to users.
"Bounce” happens when a visitor is out of the landing page on which he/she came to without going to any other page of the website. This is a sign of whether the website content is relevant, useful to the user and how to lead them to other necessary websites on your website.
With this term, many people make mistake when analyzing websites with Google Analytics. The bounce rate formula determined by Google Analytics is shown below:
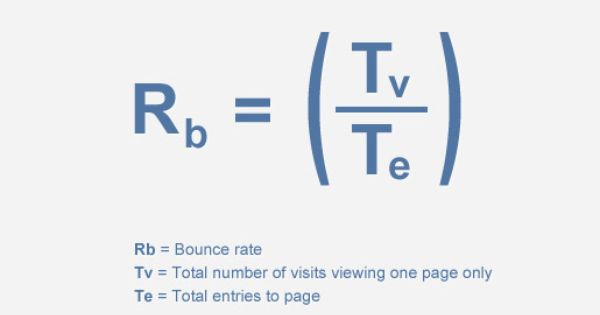
The formula of Bounce rate
Bounce rate is calculated by the total number of one-page visitors divided by the total number of entries to a website. For example, if the homepage of a website reaches 1,000 visitors over the course of a month, and 500 of those visitors leave the site after viewing the homepage without entering any other pages, then the bounce rate of that homepage would be 1000/500 = 50%.
Solution:
If your website has a high bounce rate, the reasons can be caused by many other factors such as:
• Single- page website
If your website has only one website with all the necessary items. As a result, your website will reach a high bounce rate. That time you can learn more about user behavior on page sections, you can implement an Event-driven measure of efficiency.
• Install Google Analytics script incorrectly
A common reason is that you have installed the Google Analytics code incorrectly on some web pages. In particular, if you see an exceptionally high Bounce Rate on some pages, double-check that you added the same tracking code to all pages of your website.
• Inconsistent content, design
If all your websites contain the same tracking code but you still see a high bounce rate, you can review the design, content, and add-ons, and experiences of users on the page. With the unattractive content, content does not satisfy the demand searching of customers, the bounce rate can reach up to 80%. Therefore, you need to optimize those pages so that they are tied to the search terms that bring users to your site, relative to the ads you are running. You can also change your ads or keywords toward your target customers more relevant to the content of the page.

Running the website test tools, if you ask, then “What is a Good Bounce Rate?”, there is no exact 100% answer because each type of website has a different good bounce rate
• Besides, there are other factors affecting the bounce rate such as optimize images, website loading time, optimize JS, CSS file or HTML in code, etc. To reduce this rate, you will need to take notice of many things.
Running the website test tools, if you ask, then “What is a Good Bounce Rate?”, there is no exact 100% answer for this question. With over four billion pages on the Internet, with a wide variety of website types and industries targeting a vast and diverse audience, it is difficult to generalize this metric.
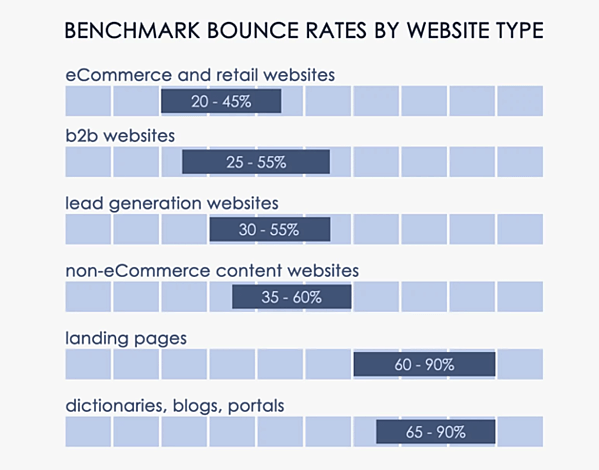
However, according to HubSpot, a rough benchmark of bounce rates by industry is compiled that represents the average bounce rate across different types of sites. With these numbers, you can have a general evaluation of your website and then find solutions to improve poor website performance.
-
40% – 60% content websites
-
30% – 50% lead generation websites
-
70% – 90% blog posts
-
20% – 40% retail / e-commerce websites
-
10% – 30% service websites
-
70% – 90% landing pages
In general, it will be better for your website if a bounce rate is below 40%. If it’s above 55%, your work definitely will focus on finding reasons why people may be leaving your site and solutions
New visitor - Returning visitor
Finally, the rate of new visitors and returning visitors can cause some misleading when analyzing metrics of Google Analytics, conducting the website test tools.
In general, users are visitors who have started one session with your website or app within a specified period of time. When you sign in/ log in to your GA account, the very first metric on the Homepage view is the number of users, which varies depending on the timeframe you choose (today, yesterday, last 7 days, etc.):
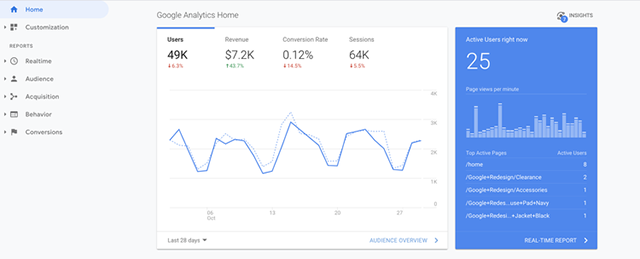
The rate of new visitors and returning visitors can cause some misleading when analyzing metrics of Google Analytics, conducting the website test tools
However, the process of Google Analytics tracking new users to the website and old users can also go wrong.
Returning users are tracked, recorded by "cookies" stored on the computer, which means that anyone who has cleared their browsing history, as well as cache cookies, will be evaluated as new users when they visit your website again.
Additionally, if a user previously visited your website from another device, that person will be counted again as a new user instead of a returning user. Of course, you will want to have more users coming back to your website because it proves that your product or service has attracted the attention of customers, not poor website performance and maybe they will gradually form buying intent. However, this metric on Google Analytics is inaccurate, Google Analytics is classifying a large number of your visitors as "new" when in fact they are returning users.
Conclusion
Using the website test tools is not enough, you will need to learn more about analysis data on Google Analysis, results of website performance testing tools to understand more customers behavior, from the effectiveness of campaigns conducted to have improvements, solutions for problems. To work well in website management along with SEO issues, let’s read more useful information on the website MySpeed.
.




0 Comments
Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *