What kind of wave is wifi? Things you may not know about Wifi
Wave brings the information from one point to another over the air. What kind of wave is wifi? How does it work? What is the feature of wave type? This article will clarify these questions.
General Introduction
What type of wave is wifi? It is radio waves. Radio waves transport information around you all the time. Wifi uses radio waves to transmit signals.
What is wifi? Wifi is wireless technology using radio waves to communicate massive amounts of data on devices over short distances.
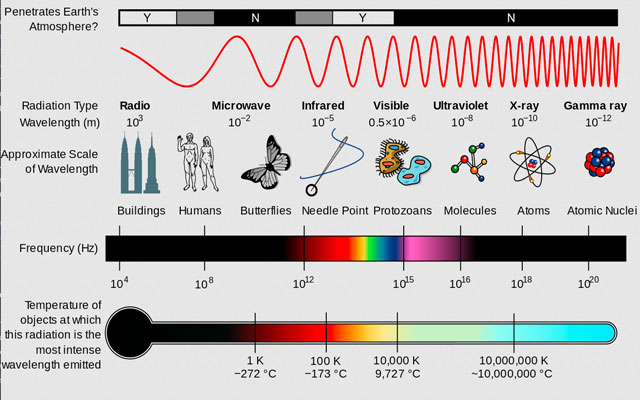
What is type of wave is wifi?
Differences between Wavelength And Frequency?
Radio waves feature the wavelength. It is the distance between identical points (adjacent crests) in adjacent cycles. This length is commonly stated in meters (m), centimeters (cm), or millimeters (mm) in wireless systems (mm).
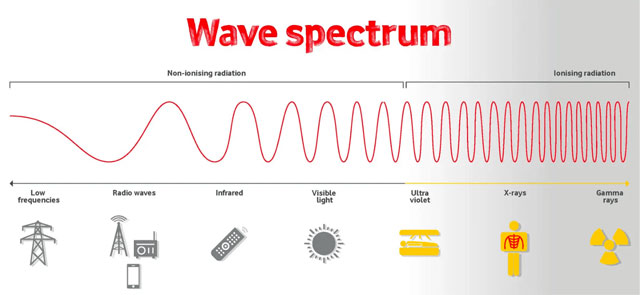
How does wave work?
Frequency, which refers to the number of wave cycles per second, is inversely related to wavelength. The shorter the wavelength, the greater the signal's frequency.
What wavelength is wifi? Wavelengths for 2.4GHz (UHF) and 5GHz (SHF) radio waves are approximately 12cm and 6cm, respectively. The decimetre wave frequency range is 2.4GHz, and the centimeter wave frequency range is 5GHz.
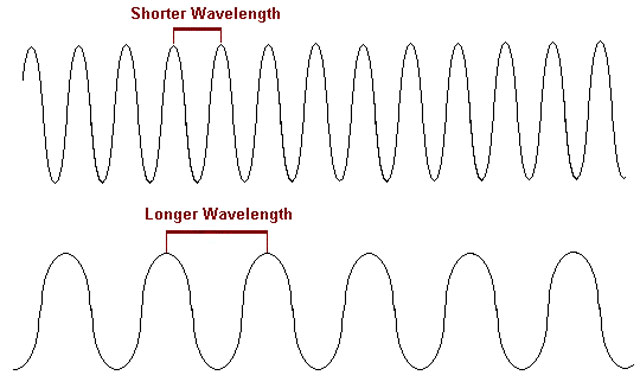
What wavelength is wifi
2.4 GHz And 5GHz Features
2.4 GHz
For Wi-Fi, the usual public highway is 2.4 GHz. It is a radio transmission that operates in the ultra-high-frequency spectrum (UHF).
UHF is a mid-range frequency that strikes a balance between longer wavelengths that are subject to upper air interference and shorter wavelengths that are easily occluded.
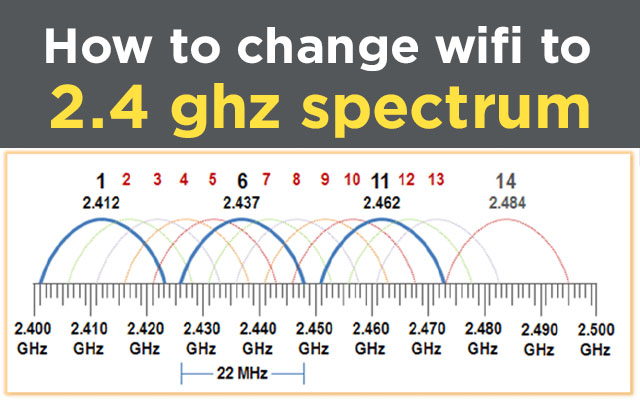
There are eleven channels in the 2.4 GHz radio frequency, with just three of them not overlapping.
Because of its wider range and stronger signal penetration, 2.4 GHz is ideal for in-home networks because it can successfully connect to devices in adjacent rooms. It also has a large coverage.
However, slower speeds, interference, and congestion can hinder this wifi frequency. a 2.4 GHz network can not meet the high-bandwidth needs.

2.4 GHz vs. 5 GHz frequency bands
5GHz
The current wifi frequency is 5 GHz, which boosts traffic faster with less congestion but only over a shorter distance. It is a type of radio signal that operates at a super-high frequency (SHF).
SHF is a frequency range that is higher than UHF. Because the SHF wavelength is so short, it is classified as a microwave.
There are over 100 channels in the 5 GHz range, with 24 of them not overlapping. Many of these channels have bandwidths ranging from 20 to 80 MHz. There is reduced congestion and interference, as well as better bandwidth performance.
Data rates of up to 1300 Mbps can be sent at 5 GHz. Its quicker speed is ideal for in-home networks that require a lot of bandwidth, such as gaming or watching videos. This positive result is clear when running a wifi speed test on your devices.
People who work from home and download or upload big volumes of data may find it handy. 5 GHz may also be the superior wifi option if you want a reliable connection, for video conferencing.
However, if you need to cover a vast area or pass through numerous walls, a 5 GHz network may be challenging to set up.
Conclusion
This article has fully explained “What kind of wave is wifi and introduced main features of the two WiFi frequency bands. Is there anything unclear?
References:
https://www.networkcomputing.com/wireless-infrastructure/wifi-networking-radio-wave-basics
https://www.techtarget.com/searchnetworking/definition/wavelength



0 Comments
Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *