Backhaul internet: Need-to-know things about backhaul network
“Backhaul internet” term appears a lot when it comes to internet connection, especially wireless networks.
A backhaul is said to improve the speed of your data communications access.
In reality, without back haul, there would be no internet connection.
So, if you’re wondering “What is a backhaul?”
Keep reading.

What is backhaul internet?
What is a backhaul?
A backhaul refers to the signal transmission from the core network to subnetworks.
Backhauling is the delivery of voice, video, and data traffic from a wireless provider's mobile base station, or cell tower, to its mobile switching center (MSC), or another central exchange point, where it is switched onto a wireline telecommunications network.
The internet and backhaul work in nearly the same way.
If the network can not handle influxes of traffic, the end-user will suffer a poor experience.
As a result, Packet loss, jitter, and high latency issues happen.
.jpg)
The definition of backhaul internet
Type of backhaul
There are several types of backhaul such as backhaul fiber, 5G backhaul, 3g backhaul, satellite backhaul,...
Usually, backhaul internet consists of 2 types: wired backhaul and wireless backhaul.
What is Wired Backhaul?
Definition
When talking about wired backhaul, people think about copper, fiber, ethernet, and coaxial to transfer the signals.
That’s why wired backhaul can also be called ethernet backhaul or ethernet backbone.
Pros:
-
Higher maximum network speeds: Both ISPs and internet users have access to the fast download speed and upload speed compared to the wireless connection.
-
Stable connection: Businesses that use wired backhaul have a better performing and more reliable connection than those that use wireless backhaul, thanks in part to less network interference.
Cons:
-
Higher cost: Wires, equipment, and installation all add up to a large bill, making the wired backhaul mesh network more expensive than the wireless counterpart.
-
Difficult to move: All of the equipment that goes into these connections imposes physical constraints. It cannot be easily moved or expanded as quickly as a wireless backhaul.

Ethernet backhaul
What is wireless backhaul?
Definition:
Wireless backhaul uses point-to-point radio or microwave or radio waves to transmit signals between access points to the end user.
Wireless backhaul is one of the most adaptable and cost-effective backhaul technology, allowing organizations to quickly install and scale as needed.
Pros:
-
Economical: When compared to wired backhaul, wireless backhaul requires fewer infrastructure assets. As a result, it is quite cost-effective. There are fewer installation and equipment costs, and it is a more affordable option overall.
-
Moveable: One of the primary reasons why wireless technology is so popular is its portability. Similarly, wireless backhaul networks are extremely easy to set up and move. If you need to relocate, you can take it with you without having to worry about installation or wiring.
Cons:
-
Slow transmission rate: Wireless backhauls are undeniably convenient, but they are not without drawbacks. The slow transmission rate is one of them. Because of their lower maximum bandwidth, wireless backhaul routers offer slower transfer speeds than their wired counterparts. It also shares network spaces between users, which slows down transmission.
-
Easily disturbed: Wireless backhauls are more susceptible to interference than wired backhauls. Because of their wireless connectivity, they are easily disrupted by various factors that can impede your workflow. It also necessitates more maintenance.
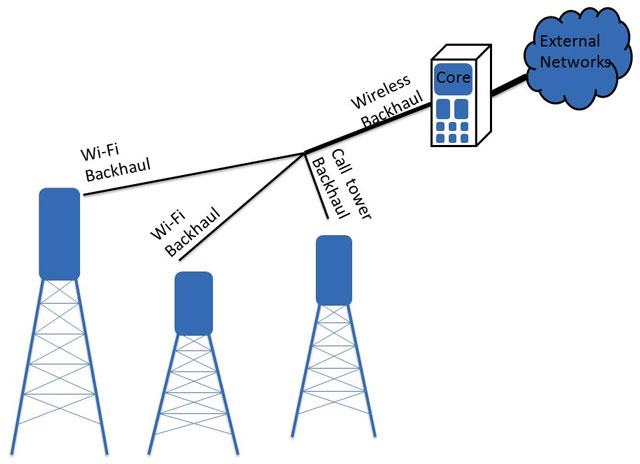
Wireless backhaul
Internet backhaul speed
-
Initial backhaul speeds
Until recently, most backhauls consisted of one or two T1 line(s) (a synchronous 1.544 Mbps data pipe) or even a T3 data circuit (the equivalent of 28 T1 lines at a speed of 44.736 Mbps) as the internet connection.
T3 circuits are also referred to as DS3 circuits.
Data compression equipment allows for much faster throughput.
-
Ethernet speed backhaul
Carriers rushed to increase the speed of their backhaul circuits to 100 Mbps.
Remember that backhaul is an expensive component of wireless cells that must be affordable in order to offer competitive data plans.
-
Fiber backhaul
Backhaul speeds of 1 Gbps or greater were required for useful data performance when 4G LTE was developed.
The providers were aware that their backhaul systems would need to be replaced.
Backhaul via fiber-optic cable provides the required speed.
The most difficult aspect of bringing in new fiber backhaul is the physical installation of the fiber, which is buried, strung on utility poles, or any other method of connecting the cell site to the internet via a massive data pipe.
Fiber-optic backhaul
-
Other backhauls
Backhaul in remote rural areas may include line-of-sight microwave links or other radio and satellite connections.
These connections, of course, support lower speeds, but if that is all you have, it is better than no connection at all.
Faster satellite and radio technologies are constantly being developed, so remote rural areas should soon be able to support 4G LTE full-speed connections.
Providers of Backhaul
Backhaul service providers include incumbent and competitive local exchange carriers (ILECs and CLECs), cable multiple system operators (MSOs), fiber service providers, and satellite service providers.
Backhaul providers include, for example:
-
ILECs & CLECs: Windstream, Lumen Technologies, and Frontier Communications Furthermore, wireless carriers such as AT&T and Verizon make their fiber available to third parties for backhaul purposes.
-
Cable Multiple System Operators (MSOs): Charter Communications, Cox Communications, and Comcast
-
Fiber providers: Conterra Networks, ExteNet Systems, Lightpath (owned by Altice USA and Morgan Stanley), Astound Broadband, Zayo, Crown Castle, Uniti Group, Segra (owned by Cox Communications), Everstream, Fatbeam, FirstLight, Consolidated Communications, BAI Communications (Mobilitie), Conterra Networks, ExteNet Systems, Lightpath (owned by Altice USA and Morgan Stanley), Astound Broadband.
-
Satellite providers: Intelsat, SES, Eutelsat, OneWeb, and possibly Starlink (SpaceX) provide higher latency mobile backhaul services, especially in rural and remote areas.

Internet service providers of Backhaul
The backbone network, also referred to as the core network, is a large fiber-optic network that connects smaller intermediate networks, such as regional and metropolitan networks.
Backhaul refers to the intermediate links that connect the backbone (core) network and the subnetworks, such as a wireless carrier's mobile base station, or cell tower, which is part of the Radio Access Network (RAN).
Backhaul is a term used to describe the transmission of a signal from a remote site or network to another, usually central, site.
Backhaul is typically associated with high-capacity lines, which are high-speed lines capable of transmitting high bandwidth at extremely fast speeds.
A network's backhaul consists of connections from the core network to subnetworks.
A backhaul connects the 5G mobile network to the wired network.
As a result, 5G backhaul refers to the signal that travels between the 5G core and remote sites or networks.
Ending words
Having understood the definition of Backhaul as well as got pros and cons of each type of backhaul internet, it’s time to decide which one should choose.
But how to choose?
If you only need a basic Internet connection with no special requirements, go with wireless backhaul to save money. It will ensure a smooth operation at a lower cost.
However, if you don't mind spending a little extra money to get the best experience possible without interruptions, go with wired backhaul.
Reference:
https://dgtlinfra.com/what-is-backhaul-wired-wireless-fiber-ethernet/



10 Comments
Alexis Turner
How about the backhaul market? You mentioned a lot about things like backhaul provider but forgot to discussed its popularity
Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *MySpeed
My fault! The fiber backhaul market is extremely competitive in urban areas. For example, there are at least 7 fiber providers in each of Boston, Denver, and Los Angeles. While there are at least 10 fiber providers in each of New York City and Washington, D.C.
Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *Alexis Turner
Thanks for your reply
Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *MySpeed
👍👍👍
Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *Lennox Brooks
Thank you for your brilliant guide. Great job! May I ask a question? What is dark fiber backhaul?
Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *MySpeed
Good question there. Dark fiber backhaul is infrastructure for wireless carriers, allowing them to create their own services, control their own network, and deliver the performance levels for their unique needs
Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *Isabella Smith
Really nice post. As always, top class and easy to read.
Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *MySpeed
Many thanks
Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *Genesis Lewis
What is Wi-Fi Backhaul?
Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *MySpeed
Wi-Fi backhaul supports small cells at the edge of a wireless carrier’s network by placing a small cell in the consumer’s home to support both in- and out-of-home wireless connectivity services
Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *